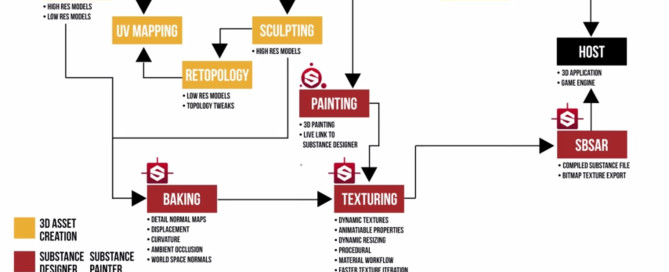
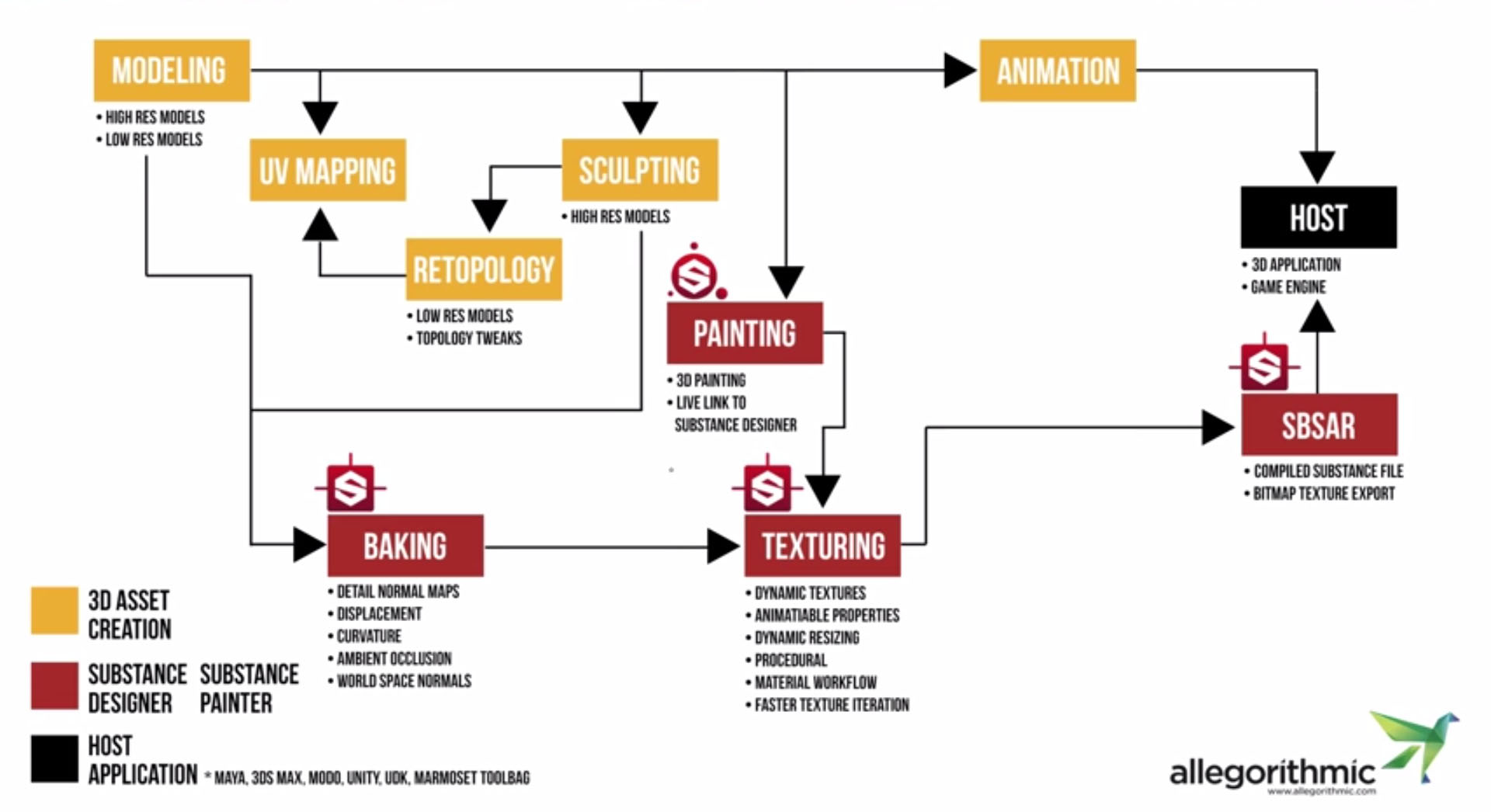
Allegorithmic Substance Painter – Basic Tutorial
Substance Painter is a mesh painter software, with this you can paint your substances over a 3D Mesh.
Let’s take it from the top!
Paint a flat color
1. Start Substance Painter
2. MAIN TOP MENU> File> New> Mesh ‘Select…’, load your .fbx file
3. LEFT COLUMN> Document Settings> setup Size, click the minus ‘-‘ on the right of the channels slots to remove unwanted channels. For now with need only ‘Base Color’.
4. LEFT COLUMN> BOTTOM LABELS ‘Viewer Settings’ and ‘Post Effects’, to setup the 3D View.
5. MAIN TOP TOOLBAR> activate ‘Symmetry’ if you need.
6. BOTTOM> Material label> select ‘plastic matte’.
7. BOTTOM> Brush label> select ‘default brush’
8. RIGHT COLUMN> Tool-Paint, as you can see we will use the brush on the left thumbnail to paint the material on the right
UNDER click on the base color slot to change color. Click over the green box under the brush thumbnail to setup the brush size, flow and spacing.
9. Go to in 3D View, paint over the mesh and remember my friend:
– LMB paint
– ALT + LMB camera rotate
– ALT + MMB camera translate
– ALT + RMB or Mouse Wheel camera zoom
– MAIUSC + LMB rotate panorama
– CTRL + RMB changes brush flow
– CTRL + LMB canges brush size
10. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> click plus ‘+’ to add a new layer, this window works like Photoshop.
We will create Layer 1 and Layer 2 for ALL CHANNELS, if you want paint only one channel you have to disable the unwanted layers inside the channel, for example select Layers> Specular> LMB over Layer 1 – Ldge (ON THE RIGHT)> Disable
11. LEFT COLUMN> BOTTOM LABELS ‘Viewer Settings’> Mode> Solo view to see only the strokes in current layer.
Paint height
1. LEFT COLUMN> Channels + Height
2. LEFT COLUMN> Viewer Settings> Height force = 1
3. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> Height> All Layer> rename it Height> Disable all aother layers
4. RIGHT COLUMN> Tool – Paint> Material – advanced> enable only ‘height’ button> Height roolout> slide to 0.6
5. Paint
use the same way to paint only specular, metallic, reflection etc…
Fill Layer
You you use a procedural substance as bricks or other seamless materials you need a fill layer
1. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> Add a Fill Layer
2. BOTTOM> Material> selec ‘bricks 001’
Mask – paint
1. RMB over the layer> Add WHITE mask (in Photoshop sarebbe aggiungi maschera> mostra tutto) and paint the mask.
Mask – decal using geometry
1. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> Select a BLACK mask layer (it turn to red)
2. MAIN TOP TOOLBAR> Geometry Decal
3. LEFT COLUMN> Viewer Settings> Wireframe opacity
4. RIGHT COLUMN> Tool – Geometry Decal> Color to white, select faces mode then select into 3D View faces
Mask – add effect (id_selector)
Apply the mask using material id
1. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> Select a BLACK mask layer (it turn to red)
2. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> TOOLBAR> Add effect> Substance effect
3. BOTTOM> LEFT> Shelf> Effects> DRAN ANG DROP ‘id_selector’ over RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> Filters parameters> ‘Effect No effect selected’ slot
You can use id material from 3DS Max of using a ID map.
Mask – add effect (MG Edge Dirt)
1. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> Select a BLACK mask layer (it turn to red)
2. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> TOOLBAR> Add effect> Substance effect
3. BOTTOM> LEFT> Shelf> Effects> DRAN ANG DROP ‘MG Edge Dirt’ over RIGHT COLUMN> Layers>
– Filters parameters> ‘Effect No effect selected’ slot
– Filters parameters> Image inputs> apply a ‘curvature map’
NOTE:
With curvature maps you can easily create masks or textures to work on chipped or worn edges.
Substance Designer creates ‘curvature maps’, based on the normal map.
Mask – Stencils
1. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> create a layer
2. BOTTOM> Shelf> Stencils> DRAG AND DROP a stencil over RIGHT COLUMN> Tool – Paint> Stencil – basic
3. BOTTOM> Shelf> Material> select a material and paint your mesh
NOTE: LEFT COLUMN> Viewer Settings> check ‘Hide stencil when painting’
Paint Stencils
1. RIGHT COLUMN> Layers> select a layer
2. BOTTOM> Shelf> Stencils> DRAG AND DROP a stencil over RIGHT COLUMN> Tool – Paint> ‘Base color’ slot
3. Use a big brush to paint your stencil!
Paint with particles
1. BOTTOM> Particles label> liquid stream
Save and Export
MAIN TOP MENU> File> Save As…, select a folder and ‘Save’
It will create a complex folder structure with all the project files.
MAIN TOP MENU> File> Export all channels> select a folder and ‘Export’
It will create a bitmap texture for every channel.
Increase Texture resolution on the fly
Substance Painter is resolution indipendent!
RIGHT COLUMN> Document Settings> Size> Change the size, Substance Painter will use the stack informations to recompute the new texture!