UNITY – JS Script – Ray casting
Ray casting is the use of ray-surface intersection tests to solve a variety of problems in computer graphics.
The first ray casting algorithm used for rendering was presented by Arthur Appel in 1968. The idea behind ray casting is to trace rays from the eye, one per pixel, and find the closest object blocking the path of that ray.
Ray casting traccia una linea da un oggetto verso l’infinito e ne rileva le intersezioni con altri oggetti. E’ come se l’oggetto avesse la capacità di vedere cosa si può intersecare con la sua traiettoria. Unity può tracciare linee di raycasting di lunghezza infinita, o limitata. Se la lunghezza è limitata tutti gli oggetti più lontani del limite imposto non saranno “visibili”. Il ray casting si basa sulla matematica dei vettori.
JAvascript Statement
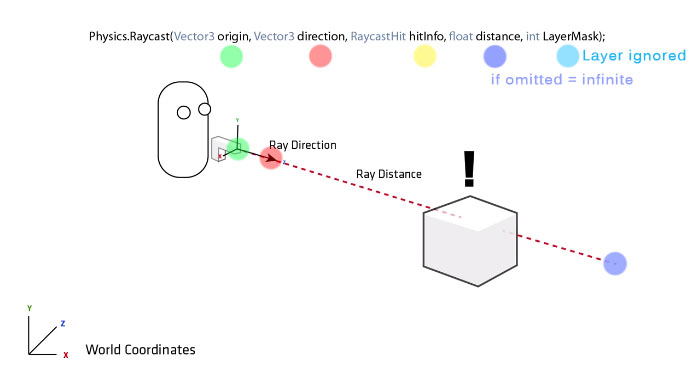
static function Raycast(origin: Vector3, direction: Vector3, hitInfo: RaycastHit, distance: float = Mathf.Infinity, layerMask: int = DefaultRaycastLayers): bool;
origin: Vector3, -> l’origine del raggio (vettore)
direction: Vector3, -> la direzione del raggio (vettore)
hitInfo: RaycastHit, -> rileva se vi sono intersezioni
distance: float = Mathf.Infinity, -> lunghezza del raggio, se omesso = infinito
layerMask: int = DefaultRaycastLayers -> layer che saranno ignorati nel Ray casting
CASE 1: Raycast Debug.Log
1. Create a Sphere that falls and bource over a Cube (You have to use Physics 3D engine)
2. Attach to the Ball the script:
#pragma strict
function Update () {
var hit : RaycastHit;
if (Physics.Raycast (transform.position, -Vector3.up, hit)) {
var distanceToGround = hit.distance;
// Casts a ray against all colliders in the scene
// and returns detailed information on what was hit
Debug.Log (distanceToGround);
}
}
CASE 2: Raycast Debug.Log + if
#pragma strict
function Update () {
// function Update START -------------------------
var hit : RaycastHit;
if (Physics.Raycast (transform.position, -Vector3.up, hit)) {
var distanceToGround = hit.distance;
// Casts the ray against all colliders in the scene
// and returns detailed information on what was hit
Debug.Log (distanceToGround);
// Distance Controller START
if (distanceToGround < 1)
{
// Do a set of actions
Debug.Log ("---- BOUNCE ----");
}
// Distance Controller END
}
// function Update END ----------------------------
}
CASE 2: Raycast Debug.Log + if + function
#pragma strict
function Update () {
// function Update() START -------------------------
var hit : RaycastHit;
// if Physics.raycast START
if (Physics.Raycast (transform.position, -Vector3.up, hit)) {
var distanceToGround = hit.distance;
// Casts the ray against all colliders in the scene
// and returns detailed information on what was hit
Debug.Log (distanceToGround);
// Distance Controller START
if (distanceToGround < 1)
{
// Call a function
Bounce();
}
// Distance Controller END
}
// if Physics.raycast END
// function Update() END ----------------------------
}
function Bounce ()
{
Debug.Log ("---- BOUNCE FUNCTION ----");;
}





